Can Anxiety Cause Sciatica? Unveiling the Connection
In the realm of sciatica, a common question arises: can anxiety cause sciatica? The answer may surprise you. Anxiety, often considered a mental health issue, can indeed manifest physically, potentially exacerbating sciatica symptoms.
Understanding Sciatica
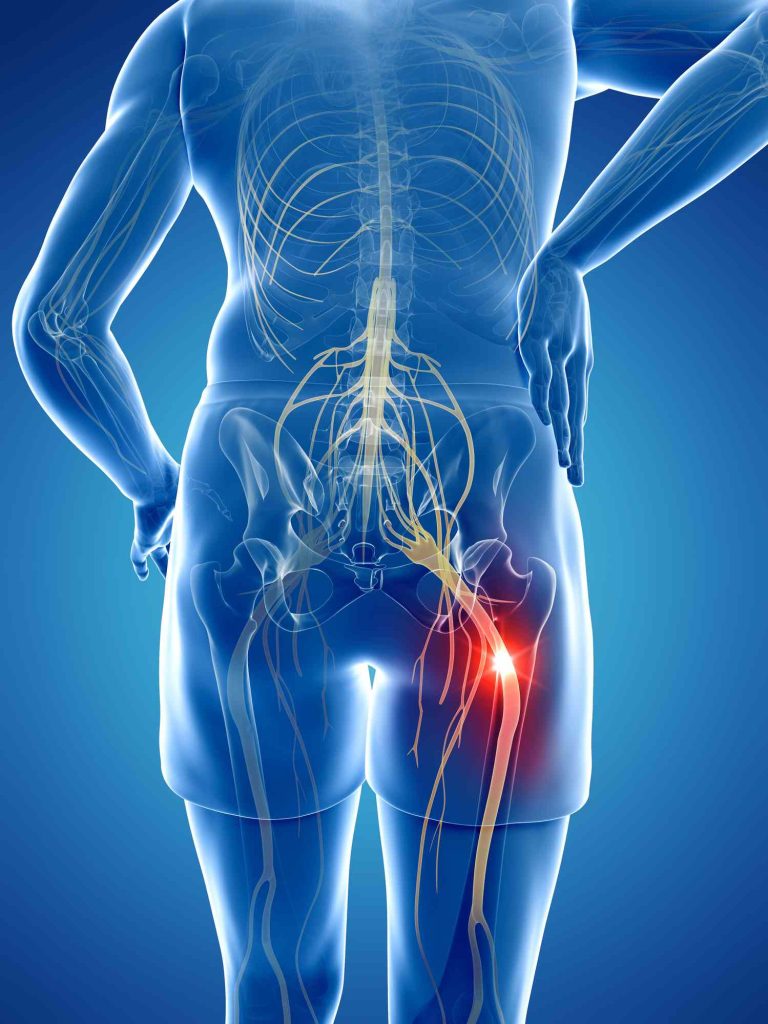
Firstly, let’s delve into what sciatica is. Sciatica refers to pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which branches from your lower back through your hips and buttocks and down each leg. It’s often caused by a herniated disk, bone spur on the spine, or narrowing of the spine.
The Link Between Anxiety and Physical Pain
Anxiety, characterized by excessive worry and fear, can have profound effects on the body. Research suggests that anxiety can contribute to muscle tension, inflammation, and heightened perception of pain. These effects can exacerbate sciatica symptoms and prolong recovery.
Understanding the Mind-Body Connection
The mind-body connection is a well-studied phenomenon in the medical field. Stress and anxiety can trigger physical responses in the body, including increased muscle tension and changes in hormone levels. These responses can worsen existing conditions like sciatica.

Research Findings
Studies have shown a significant association between anxiety and the severity of sciatica symptoms. Research found that individuals with higher levels of anxiety reported increased pain intensity and disability related to sciatica.
The Role of Stress Hormones
When we experience anxiety, our bodies release stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones can heighten sensitivity to pain and exacerbate inflammation, potentially worsening sciatica symptoms. The prolonged presence of stress hormones can also impede the body’s natural healing processes.
Impact on Physical Functioning
Anxiety can also affect physical functioning, leading to decreased mobility and activity levels. This can perpetuate a cycle of pain and inactivity, further exacerbating sciatica symptoms. Addressing anxiety alongside sciatica treatment is crucial for improving overall functioning and quality of life.
Addressing Anxiety in Sciatica Treatment
Treating sciatica involves addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition. While medical interventions like physical therapy and medication can alleviate physical symptoms, addressing anxiety is equally important for comprehensive treatment.
Psychological Interventions
Therapeutic interventions such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can be effective in managing anxiety and its impact on sciatica. CBT helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and develop coping strategies to manage anxiety and pain effectively.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Practices like mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce anxiety levels and promote relaxation. Incorporating these techniques into daily routines can complement traditional sciatica treatments and improve overall well-being.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle changes to reduce stress and promote relaxation can also benefit individuals with sciatica and anxiety. Prioritizing adequate sleep, maintaining a healthy diet, and engaging in regular exercise can help manage both physical and emotional symptoms.

Seeking Support
Support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends is essential for individuals managing sciatica and anxiety. Open communication with healthcare providers about symptoms and treatment preferences can ensure holistic care and better outcomes.
Conclusion: Addressing the Mind-Body Connection
In conclusion, the answer to the question “can anxiety cause sciatica pain?” is affirmative. Anxiety can exacerbate sciatica symptoms through various physiological and psychological mechanisms. By addressing anxiety alongside traditional sciatica treatment, individuals can experience improved pain management and overall well-being.
At Medcareline.com, we understand the complexities of managing sciatica and offer valuable resources and informational posts to support individuals on their journey to recovery. Together, let’s navigate the intricacies of sciatica and anxiety to achieve optimal health and wellness.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can anxiety medication help alleviate sciatica symptoms?
A: While anxiety medication primarily targets mental health symptoms, some medications, such as muscle relaxants or antidepressants, may also provide relief for both anxiety and sciatica symptoms. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Q2: Does cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) specifically target sciatica pain?
A: CBT primarily focuses on addressing negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with anxiety. While it may not directly target sciatica pain, CBT can help individuals develop coping strategies to manage the psychological impact of chronic pain, including sciatica.
Q3: Are there specific relaxation techniques that can help alleviate sciatica-related anxiety?
A: Yes, various relaxation techniques, such as mindfulness meditation, guided imagery, and progressive muscle relaxation, can help reduce anxiety levels and promote relaxation. These techniques may indirectly alleviate sciatica-related anxiety by calming the nervous system and reducing overall stress levels.
Q4: Can stress exacerbate sciatica symptoms even without underlying anxiety disorders?
A: Yes, stress can exacerbate sciatica symptoms even in individuals without diagnosed anxiety disorders. Stress triggers physiological responses in the body, including increased muscle tension and inflammation, which can worsen sciatica pain. Therefore, managing stress through relaxation techniques and lifestyle modifications is essential for managing sciatica symptoms.
Q5: Is there a correlation between anxiety levels and the effectiveness of sciatica treatments?
A: Research suggests that higher levels of anxiety may impact the effectiveness of sciatica treatments. Individuals with higher anxiety levels may experience greater pain intensity and disability, potentially influencing treatment outcomes. Addressing anxiety alongside sciatica treatment may lead to improved overall outcomes and symptom management.






I’m thoroughly captivated with your keen analysis and stellar writing style. Your expertise clearly stands out in each paragraph. It’s evident that you spend considerable time into understanding your topics, and this effort is well-appreciated. Thanks for providing such detailed information. Keep on enlightening us! https://rochellemaize.com
I’m truly impressed with your profound understanding and excellent writing style. Your expertise shines through in every piece you write. It’s clear that you put a lot of effort into researching your topics, and that effort does not go unnoticed. Thanks for providing this valuable knowledge. Keep on enlightening us! https://www.elevenviral.com